Brief Introduction to Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that enables developers to build, test, and deploy their software reliably. It facilitates continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) by automating the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, thereby allowing teams to integrate changes more frequently and with higher confidence.
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that enables developers to build, test, and deploy their software reliably. It facilitates continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) by automating the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, thereby allowing teams to integrate changes more frequently and with higher confidence.
VM Specifications
- Hostname: jen01
- CPU: 1
- Memory: 1 GB
- Disk: 16 GB
- Internal IP: 172.16.1.252
- External IP: 172.16.1.252
- User: root
- Password: redhat
1. Install Java, wget, and rsyslog:
# dnf install java-17-openjdk-devel wget rsyslog
2. Start rsyslog service:
# systemctl start rsyslog
3. Add Jenkins repository:
# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat/jenkins.repo
4. Import Jenkins GPG key:
# rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat/jenkins.io-2023.key
5. Install Jenkins:
# dnf install jenkins
6. Start Jenkins service:
# systemctl start jenkins
7. Enable Jenkins to start on boot:
# systemctl enable jenkins
8. Check Jenkins service status:
# systemctl status jenkins
9. Access Jenkins
Open a browser and navigate to http://jen01.darole.org:8080
Retrieve the Initial Admin Password
To unlock Jenkins, you need to retrieve the initial admin password from the Jenkins server.
# cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Copy the password displayed in the terminal.
Post-Installation Configuration
10. Install Suggested Plugins
On the "Customize Jenkins" page, select "Install suggested plugins."
Jenkins will automatically install the recommended plugins. This may take a few minutes.
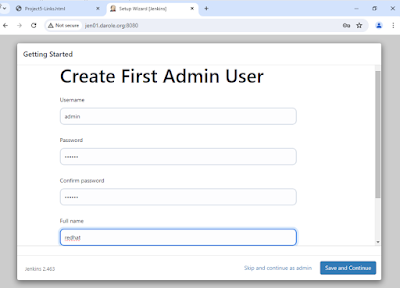
11. Create the First User
Once the plugins are installed, you will be prompted to create the first Jenkins user.
Fill in the following fields:
- Username: admin
- Password: redhat
- Full name: administrator
- Email: ansible@pup01.darole.org
Click "Save and Finish."
12. Configure Jenkins URL
On the "Instance Configuration" page, set the Jenkins URL to http://jen01.darole.org:8080/.
Click "Save and Finish."
13. Jenkins is Ready
You will see a confirmation page indicating that "Jenkins is ready!"
Click "Start using Jenkins" to proceed to the Jenkins dashboard.
14. Jenkins Dashboard
You will now be directed to the Jenkins dashboard, where you can start creating jobs, managing configurations, and utilizing all the features Jenkins offers.
Jenkins Agent Installation and Configuration.
Steps 1: Configure Security Setting
- Click on Manage Jenkins.

- Scroll Down to Security.
- Under Security settings, go to Agents and Select TCP port for inbound agents as "Random", then Save and exit.
- Enter the node name as dock01 (since we are implementing it on the dock01 node). Select Permanent Agent and click on Create.
- Set the Remote root directory to /root/jenkins.(Ensure this directory is created on the dock01 node as well.) Click Save and Close.
- Click on dock01 to configure the agent.
- After clicking on dock01, you will see the agent connection command.
- Copy the command and execute it on the dock01 server. Run the following commands sequentially on dock01:
root@dock01:~# apt update
root@dock01:~# apt install default-jre
root@dock01:~# apt install openjdk-17-jre-headless
root@dock01:~# curl -sO http://jen01.darole.org:8080/jnlpJars/agent.jar
root@dock01:~# java -jar agent.jar -url http://jen01.darole.org:8080/ -secret 8331411ab4e1600c2e15067f0cb5ad345713d78436f6c40d71cb5f7c9290cca7 -name dock01 -workDir "/root/jenkins"&
- Once the commands are executed, the agent installation will be completed. You should see the dock01 node details in Jenkins.
Building and Deploying Docker Projects in Jenkins
Deploying the "Travel-Site" Project
Step1: Create a New Project
1. Navigate to the Jenkins Dashboard
2. Click on New Item.

Step 2: Configure Project
- Name the project travel-site.
- Select Freestyle Project and click OK.
Step 3: Configure Source Code Management
On the project configuration page:
- Set GitHub project with the URL: https://github.com/vdarole/jenkin.git.
- Under Source Code Management, choose Git and provide the repository URL: https://github.com/vdarole/jenkin.git.
- Specify the branch to build as */main.
Step 4: Restrict Project to Run on Specific Nodes
Check Restrict where this project can be run.
Enter dock01 in the field to ensure this project runs on the dock01 node.
Step 5: Add Build Steps
Under Build, select Execute Shell.
Paste the following script:
docker build -t nginx_ubuntu .
docker container run --name travel -dit -v /git-data/web-temp/Travel/:/var/www/html -p 172.16.1.218:80:80 nginx_ubuntu
docker exec -d travel /usr/bin/systemctl start nginx
Save and exit.
Step 6: Save and Trigger Build
Click Save and then Build Now.
Step 7: Monitor Build Output
Once the build starts, click on the Build Number under Build History.
Navigate to Console Output to monitor the build progress.
Step 8: Verify Deployment
Log in to the dock01 server and check the Docker container status using the following command:
root@dock01:~# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
58237a873ade nginx_ubuntu "/bin/bash" About a minute ago Up About a minu te 172.16.1.220:80->80/tcp carvilla
b501cda42533 nginx_ubuntu "/bin/bash" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 172.16.1.218:80->80/tcp travel
root@dock01:~#
Building and Deploying Java Projects using Jenkins
Introduction
In this blog, we will walk through the steps to build and deploy Java projects using Jenkins. We'll set up agents for development and production environments, configure Maven, and create both freestyle and pipeline projects to automate the build and deployment process.
Setting Up Jenkins Agents
Step 1: Add a New Development Node
1. Navigate to Dashboard > Manage Jenkins > Nodes.
2. Click New Node.
3. Enter the node name as tomd01.
4. Select Permanent Agent and click Create.
5. Set the Remote root directory to /tmp. Ensure this directory exists on the tomd01 node.
6. Click Save and Close.
Step 2: Configure the Agent
Click on tomd01 to configure the agent.
Copy the agent connection command provided in Jenkins.
Execute the following commands on the tomd01 server:
root@tomd01:~#apt update
root@tomd01:~#apt install default-jre
root@tomd01:~#apt install openjdk-17-jre-headless
root@tomd01:~#curl -sO http://jen01.darole.org:8080/jnlpJars/agent.jar
java -jar agent.jar -url http://jen01.darole.org:8080/ -secret 652c3f8fc5c8b9e53a709a1421f8f895008bb364bfdced -name tomd01 -webSocket -workDir "/tmp" &
Step 3: Add Production Node
Follow the same procedure to add the production node tomp01.
Once completed, you should see both tomd01 and tomp01 nodes in Jenkins.
Installing Maven on Jenkins Server
Step 1: Install Maven
Run the following commands on the Jenkins server (jen01):
[root@jen01 ~]# yum install maven
[root@jen01 ~]# update-alternatives --config java
Selection Command
-----------------------------------------------
* 1 java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.452.b09-2.el8.x86_64/jre/bin/java)
+ 2 java-17-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-17.0.15.0.6-2.el8.x86_64/bin/java)
Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number: 2
[root@jen01 ~]#
Step 2: Configure Maven in Jenkins
1. Navigate to Manage Jenkins > Tools Configuration.
2. Under Maven, add a new Maven installation (e.g., maven-3.5.4).
3. Save the configuration.
Creating a Freestyle Maven Project
Step 1: Create the Project
1. Navigate to the Jenkins dashboard.
2. Click New Item.
3. Enter the project name (e.g., freestyle-maven-project).
4. Select Freestyle Project and click OK.
Step 2: Configure the Project
1. GitHub Project URL:
https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war.git/
2. Restrict where this project can run:
tomd01
3. Source Code Management:
Repository URL:
https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war.git
4. Branch Specifier:
*/master
Step 3: Add Build Steps
Under Build, select Execute Shell and add the following script:
rm -rf /git/tomcat-war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp
cd /git
git clone https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war.git
sed -i 's/Project/Project: Freestye Maven Project /g' /git/tomcat-war/src/main/webapp/index.jsp
cd tomcat-war
mvn compile
mvn test
mvn package
cp /git/tomcat-war/target/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war /opt/tomcat/webapps/
Step 4: Save and Build
Before building the project, update the GitHub repository with the current date and time(https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war/blob/master/src/main/webapp/index.jsp ).
Click Save and then Build Now to trigger the build.
Verify the links
Creating a Maven Pipeline Project
Step 1: Create the Pipeline Project
1. Navigate to the Jenkins dashboard.
2. Click New Item.
3. Enter the project name (e.g., maven-pipeline-project).
4. Select Pipeline and click OK.
Step 2: Configure the Pipeline Script
Use the following pipeline script:
pipeline {
agent { label 'tomd01' } // Ensure this label matches your Jenkins agent configuration
tools {
maven 'maven-3.5.4' // Ensure Maven is configured in Jenkins under "Global Tool Configuration"
}
stages {
stage("Clean up directories") {
steps {
sh '''
rm -rf /git/tomcat-war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp
'''
}
}
stage("Clone the repository") {
steps {
sh '''
cd /git
git clone https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war.git
'''
}
}
stage("Build the project") {
steps {
sh '''
cd /git/tomcat-war
sed -i 's/GIT/GIT(Jenkin)/g' /git/tomcat-war/src/main/webapp/index.jsp
mvn compile
mvn test
mvn package
'''
}
}
stage("Deploy to Tomcat") {
steps {
sh '''
cp /git/tomcat-war/target/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war /opt/tomcat/webapps/
'''
}
}
}
}
Step 3: Save and Build
Before building the project, update the GitHub repository with the current date and time.
Click Save and then Build Now to trigger the pipeline.
Verify the links
Creating a Maven Production Pipeline
Step 1: Create the Pipeline Project
1. Navigate to the Jenkins dashboard.
2. Click New Item.
3. Enter the project name (e.g., maven-production-pipeline).
4. Select Pipeline and click OK.
Step 2: Add Parameters
Check This project is parameterized and add a Choice Parameter:
Name: ENV
Choices:
DEV
PROD
Step 3: Configure the Pipeline Script
Use the following pipeline script:
pipeline {
parameters {
choice(name: 'ENV', choices: ['DEV', 'PROD'], description: 'Select the environment to deploy to')
}
agent {
label "${params.ENV == 'DEV' ? 'tomd01' : 'tomp01'}"
}
tools {
maven 'maven-3.5.4'
}
stages {
stage("Clean up directories") {
steps {
sh '''
rm -rf /git/tomcat-war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war
rm -rf /opt/tomcat/webapps/SimpleTomcatWebApp
'''
}
}
stage("Clone the repository") {
steps {
sh '''
cd /git
git clone https://github.com/vdarole/tomcat-war.git
'''
}
}
stage("Build the project") {
steps {
sh '''
cd /git/tomcat-war
sed -i 's/Project/Project : Maven-Pipeline Project/g' /git/tomcat-war/src/main/webapp/index.jsp
mvn compile
mvn test
mvn package
'''
}
}
stage("Deploy to Tomcat") {
steps {
sh '''
cp /git/tomcat-war/target/SimpleTomcatWebApp.war /opt/tomcat/webapps/
'''
}
}
}
}
Step 4: Save and Build
Before building the project, update the GitHub repository with the current date and time.
Click Save and then Build Now to trigger the pipeline.
Verify the links
Conclusion
By following this guide, you can efficiently build and deploy Java projects using Jenkins. The setup ensures a smooth CI/CD process with separate environments for development and production. Let me know if you have any questions or need further assistance!



































No comments:
Post a Comment